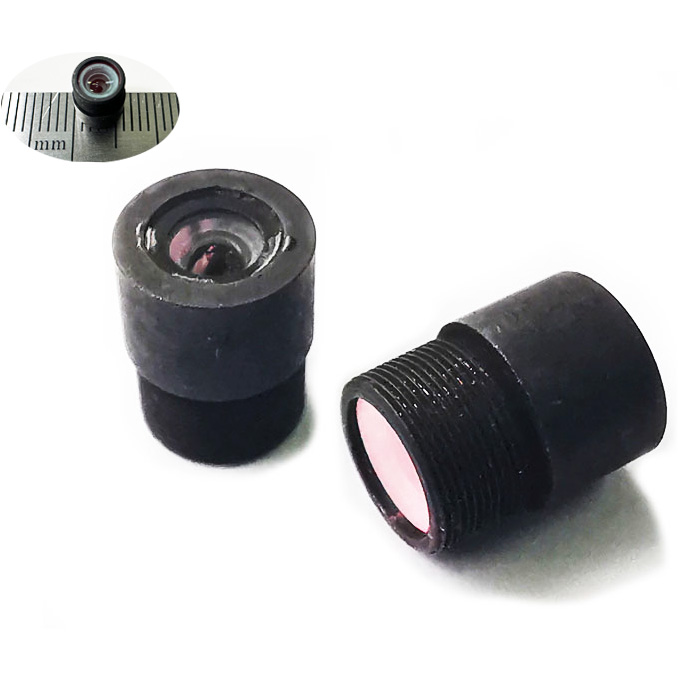
What is an endoscope lens, and how does it work?
2024-12-18
An endoscope lens is a tubular device equipped with a light that can be inserted into the human body through natural orifices or surgical incisions to observe and diagnose the condition of internal organs and tissues.
The working principle of an endoscope lens involves several key components and technologies:
Optical system: Endoscopes are usually equipped with optical lenses to capture and transmit images. These lenses can be hard or soft, with hard lenses providing better image quality but poorer flexibility, and soft lenses providing slightly inferior image quality but being easier to bend inside the body.
Light source: The endoscope transmits light through optical fibers to illuminate the area to be examined. One end of the optical fiber receives light from an external light source, and the other end transmits the light to the front end of the endoscope to illuminate the tissue inside the body.
Image transmission: Modern endoscopes are usually equipped with image sensors (such as CCD or CMOS chips) that capture the images captured by the lens and convert them into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then transmitted to an external monitor or computer for the doctor to observe and analyze.
Operation method: The endoscope can be controlled by the operating unit, and the doctor can adjust the direction and angle of the endoscope through the operating unit to better observe the target area. In addition, some advanced endoscopes are equipped with micro-integrated circuit sensors that can feed back the observed information to the computer for more complex analysis and processing.
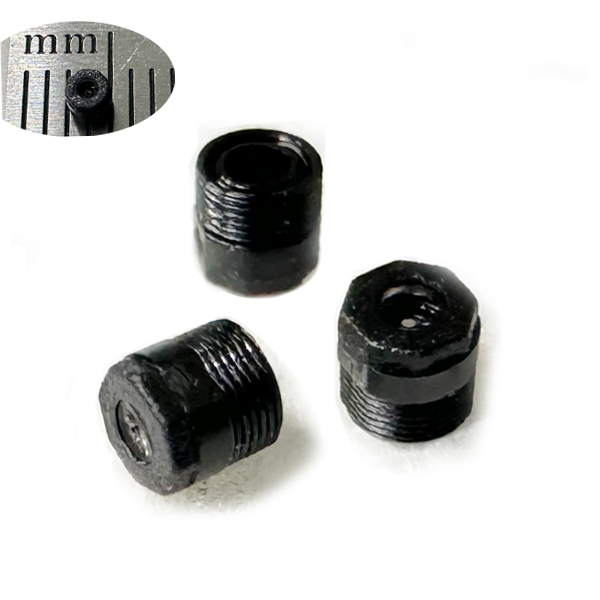

History and application of endoscope lenses
The history of endoscopes can be traced back to 1853, when it was created by French doctor Desomio. The original endoscope was a hard tube, which was later improved to a soft tube in the 1950s to make it easier to bend inside the body. In 1965, Harold Hopkins installed a cylindrical lens on the endoscope to further improve the clarity of the field of view.
Different types of endoscope lenses and their applications
Endoscope lenses can be divided into many types according to different application scenarios and technologies:
Medical endoscopes: used to diagnose and treat diseases inside the human body, such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy, etc.
Industrial endoscopes: used to inspect the internal conditions of mechanical equipment and structures, such as automobile engines, fuel systems, etc.